Traces of life in a meteorite from Mars
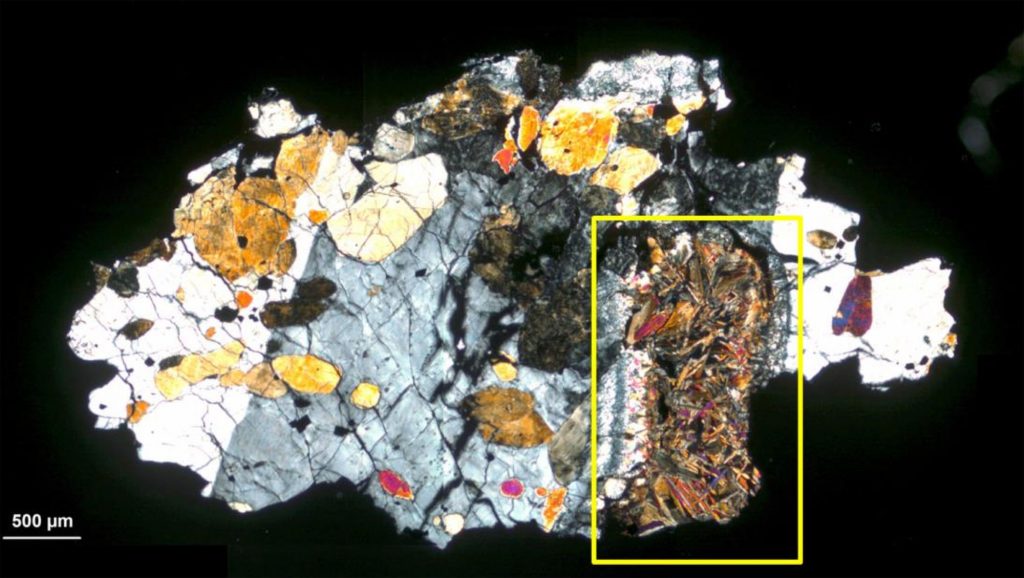
ALH-77005 has already been through a lot. The lump of stone, which weighs around one pound, was ripped from the surface of Mars 178 million years ago by the impact of a bigger meteorite. The force of the impact flung it into space. Through no fault of its own, ALH-77005 was then put on a course to Earth, where it arrived three million years later. It was bigger at the time, but its entry into the Earth’s thick atmosphere would have broken it apart. A lump of brown-gray stone, weighing 483 grams and measuring 9.5 cm x 7.5 cm…