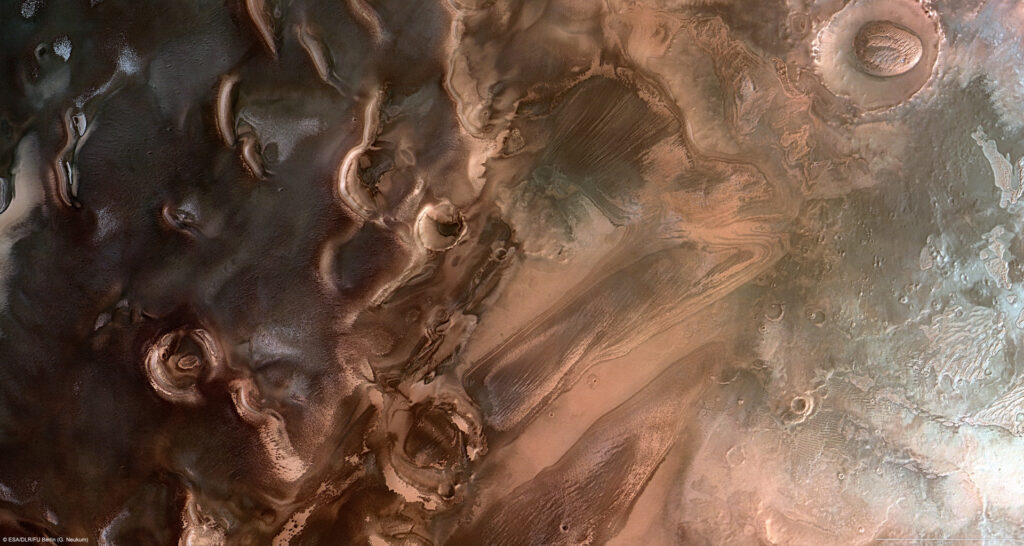
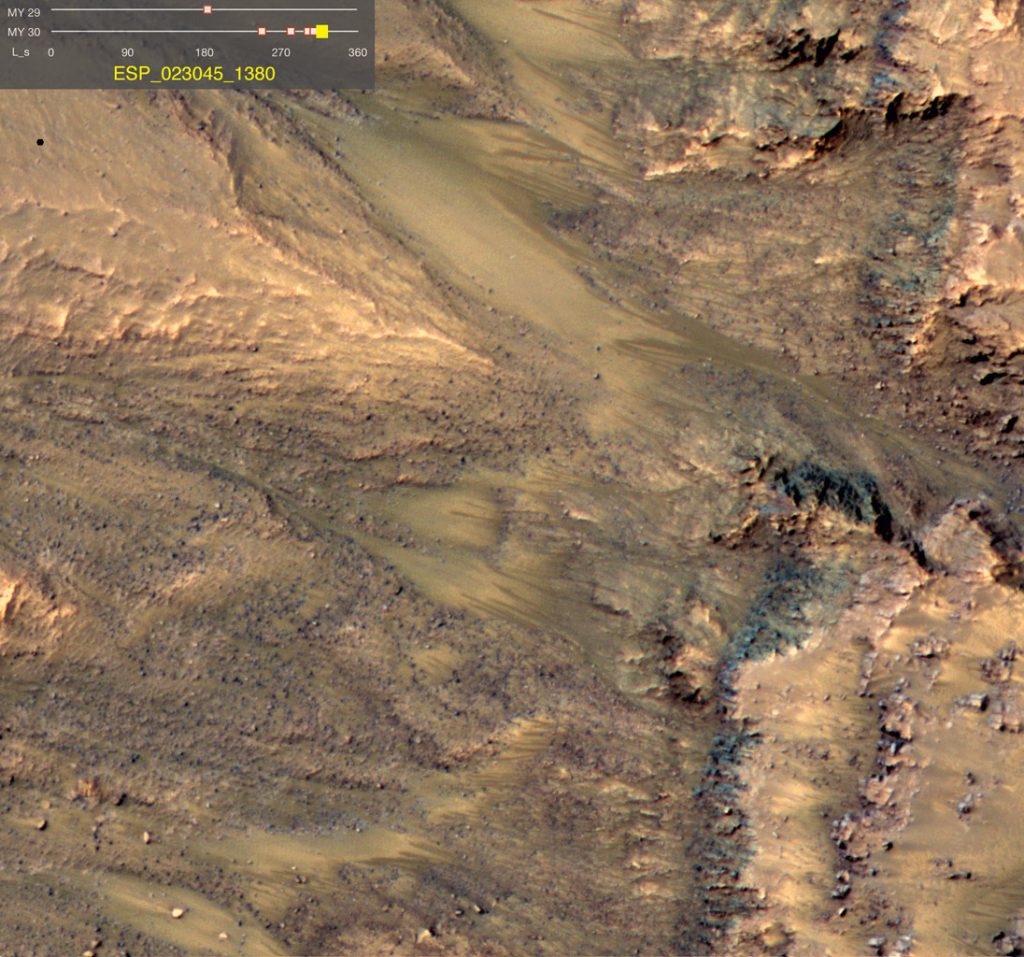
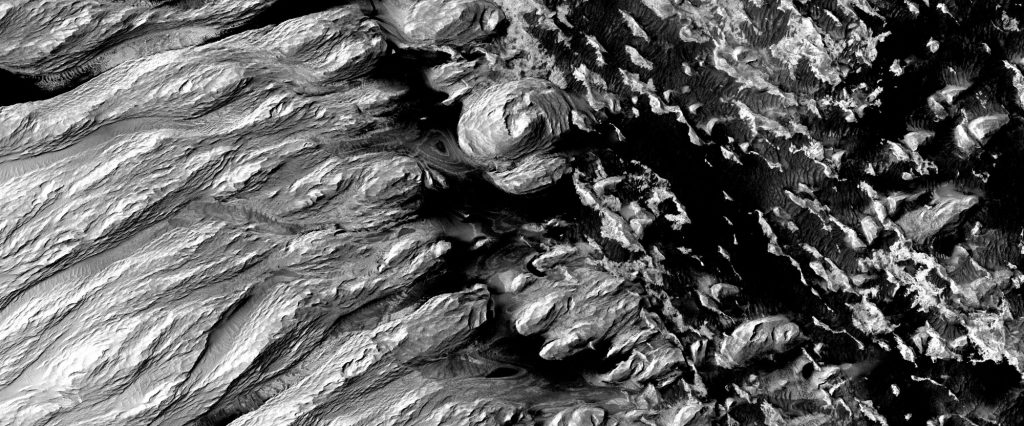
Salt lakes under the south pole of Mars
Several liquid deposits of different sizes have been discovered by researchers below the south pole of Mars, according to a publication published in Nature Astronomy. The results suggest that there may be lakes below the south pole of Mars that remain liquid due to their high salt concentration. It is known that subglacial lakes exist in the terrestrial Antarctic. Previous research has shown a similar lake below the southern Martian polar region, which was discovered by the Mars Advanced Radar for Subsurface and Ionosphere Sounding (MARSIS) on board the spacecraft Mars Express. The presence of a subglacial lake could…