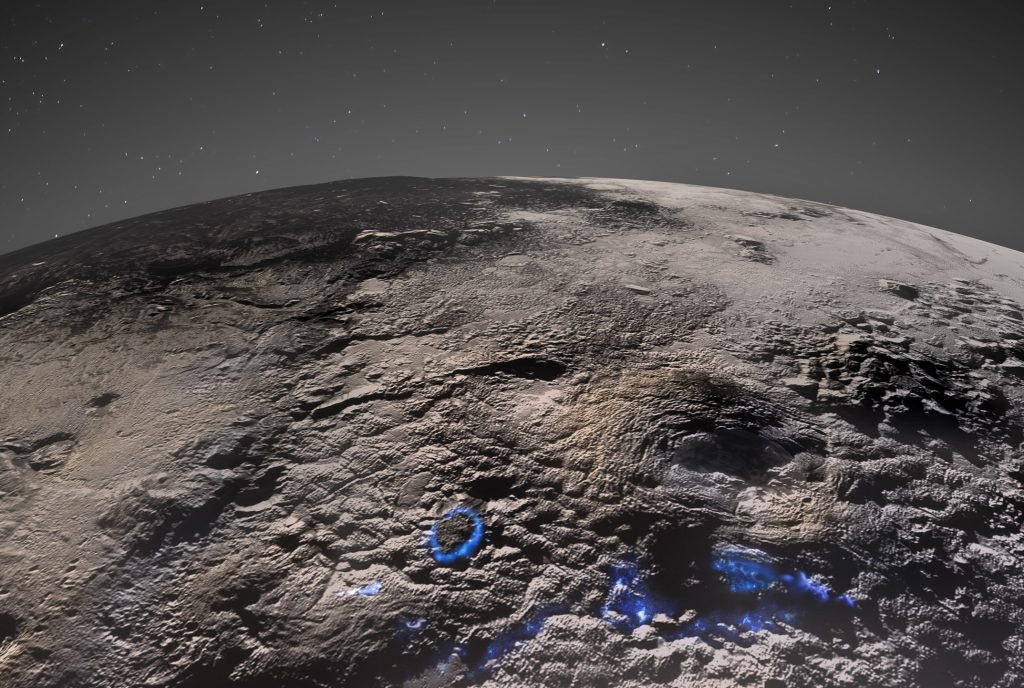
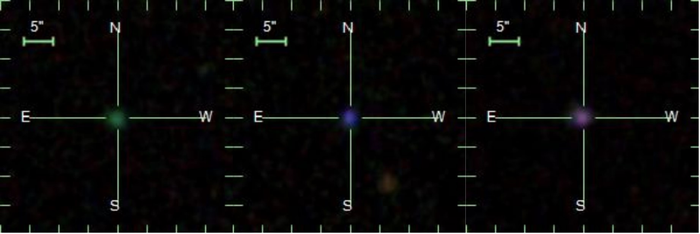
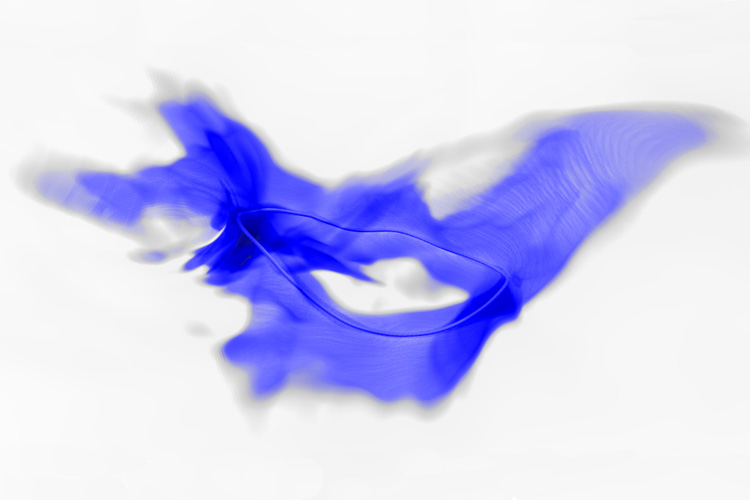
4 mile high ice volcanoes on Pluto
The exploration of the dwarf planet Pluto is divided into two eras: Before the arrival of NASA's New Horizons probe, the celestial body was thought to be an icy, unspectacular Kuiper Belt object. But New Horizons then delivered images and data that sent astronomers into raptures. The composition of Pluto's surface shows that there are a variety of ages here, from relatively old, heavily cratered regions to very young surfaces with few to no impact craters. One of the regions with very few impact craters is dominated by huge mountains with humpbacked flanks not found anywhere else in the…