Did life come from outer space?
How did the building blocks of life come about on Earth? So far, science has not given a very exact answer to this question. The most important experiment on this question was conducted in 1952 by Stanley Miller and Harold Urey at the University of Chicago. They mixed together simple chemical substances of a hypothetical young Earth atmosphere – water, methane, ammonia, hydrogen, and carbon monoxide, but no oxygen – and exposed this mixture to electrical discharges that were meant to replicate the energy supplied from lightning in thunderstorms. The result: after some time, organic molecules were produced.
At the time, the Miller-Urey experiment caused quite a stir, it seemed to show that under the right conditions, the building blocks necessary for the creation of life could form spontaneously. However, geologists later showed that in its early days, the Earth had somewhat different conditions. In addition, the results did indeed show amino acids, but no carbohydrates or lipids (fats), which are other important building blocks of life. For all these components, chemists have in the meantime found ways how they could have been formed from the chemicals originally present, but the location where all these came together has been missing.
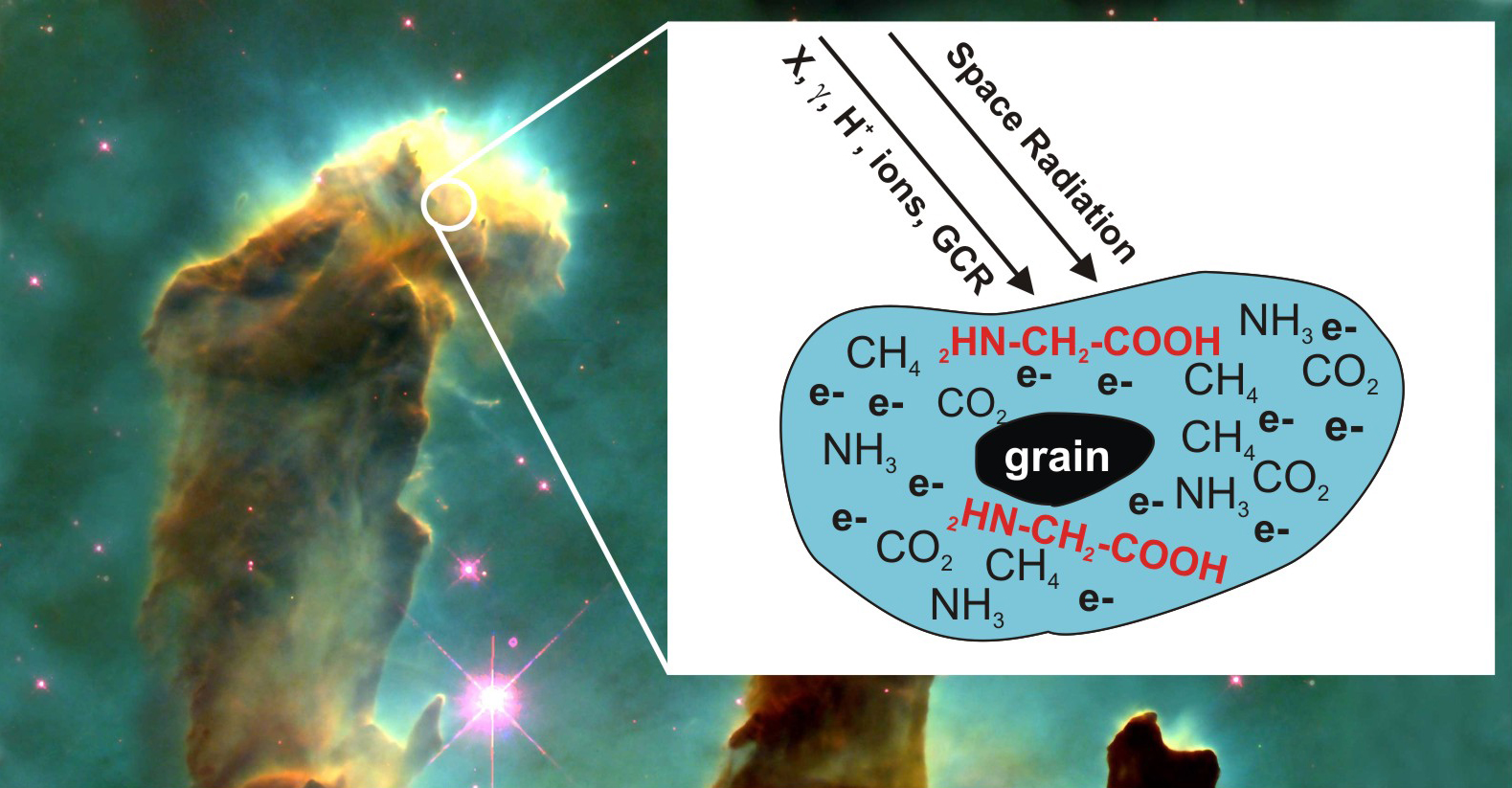
Could it have happened in outer space? Some scientists consider it possible. In fact, basic simple building blocks have already been discovered in space. In a scientific article, a team of Canadian scientists has now shown even a (simple) amino acid, glycine, can be produced in space. For this experiment, the scientists exposed the raw materials in the laboratory to a bombardment of low-energy electrons released by the ionization of matter by radiation. The reaction rate was so high that realistic quantities of glycine could be produced that could eventually be deposited on a planet.
“You have to remember — in space, there is a lot of time,” Michael Huels, one of the scientists, explains. “The idea was to get a feel for the probability: is this a realistic yield, or is this a quantity that is completely nuts, so low or so high that it doesn’t make sense? And we find that it is actually quite realistic for a rate of formation of glycine or similar biomolecules.”